STAGING THE DISEASE
Staging determines the extent of prostate cancer. Localized prostate cancer means that the cancer is confined within the prostate. Locally advanced prostate cancer means that most of the cancer is confined within the prostate, but some has started to escape to the immediate surrounding tissues such as the capsule or seminal vesicles. In metastatic disease, the prostate cancer is growing outside the prostate and its immediate environs, often to lymph nodes but possibly to more distant organs. Lymph nodes are normal parts of the body that fight off infection. Lymphatic ducts connect organs like the prostate to lymph nodes, and prostate cancer can occasionally move along these ducts to spread into lymph nodes. There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Prostate cancer tends to spread first, if at all, to lymph nodes in the lower abdomen and pelvis. These can typically be seen using imaging studies.
A number of tests can be used to help determine the stage of disease. For example, cancers growing outside of the prostate can often be detected through traditional imaging studies, such as CT scans (see image), MRIs, or x-rays, or through more specialized imaging tests such as bone scans. Note that because these tests cannot detect very small groups of cancer cells, results of these tests cannot be used alone to determine the stage of the disease, to guide treatment options, or to predict outcomes.
Metastatic disease can also be detected through imaging studies, and often can be detected in the lymph nodes. Cancers that spread to more distant organs tend to travel through the lymph system, a circulatory system similar to the blood stream that carries cells important in fighting infection and disease. During a biopsy, or, more often, during surgery, lymph nodes will be removed and examined for the presence of cancer cells.
Knowing the stage of disease can help to determine how aggressively the disease needs to be treated, and how likely it is to be eradicated by the available treatment options.
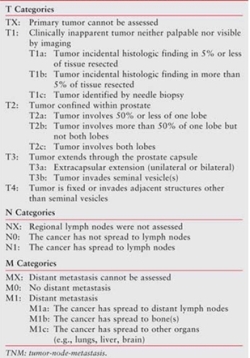
In prostate cancer, we typically talk about localized disease (stage T1-T4) and metastatic disease (stages N1 and M1). The T score describes how much the prostate cancer has spread within the prostate and its surrounding structures. The N score describes if lymph nodes are involved with cancer, and the M score describes if cancer has spread to areas outside of the pelvis, like bone. We also refer to a clinical staging score which can be performed before surgery or radiation, and a surgical staging score, which can only be provided after surgery. Most men are currently diagnosed with clinical stage T1c, meaning that their cancers were diagnosed by PSA screening only, and are not detectable by imaging or by examination.
In general, we also talk about localized prostate cancer based on risk. Men with low risk prostate cancer will have a clinical T1c-T2a stage, a PSA under 10 ng/dl, and a Gleason sum of under 7. These men have a very low risk of dying from prostate cancer and generally do well with most forms of therapy, including active surveillance. Current clinical trials are attempting to show which of these men need definitive therapy and which men can be safely observed. This is the most common form of prostate cancer.
Men with high risk prostate cancer have clinical T2c and higher stage,
Gleason 8 or higher grade, and PSA over 20 ng/dl.These men have a much higher risk of recurrence with surgery or radiation or surveillance, and often benefit from more aggressive combination approaches, and often clinical trials are attempting to improve upon these outcomes.
Men with intermediate risk prostate fall in between, and have a PSA between 10 and 20 ng/dl, a clinical stage of T2b, and a Gleason 7 grade. Men with this kind of cancer are likely to benefit from treatment (surgery, radiation, seeds) and do well with this treatment.
See the figure to the right which describes the staging system.
PROSTATE CANCER FOUNDATION www.pcf.org
 Gleason 8 or higher grade, and PSA over 20 ng/dl.These men have a much higher risk of recurrence with surgery or radiation or surveillance, and often benefit from more aggressive combination approaches, and often clinical trials are attempting to improve upon these outcomes.
Men with intermediate risk prostate fall in between, and have a PSA between 10 and 20 ng/dl, a clinical stage of T2b, and a Gleason 7 grade. Men with this kind of cancer are likely to benefit from treatment (surgery, radiation, seeds) and do well with this treatment.
Gleason 8 or higher grade, and PSA over 20 ng/dl.These men have a much higher risk of recurrence with surgery or radiation or surveillance, and often benefit from more aggressive combination approaches, and often clinical trials are attempting to improve upon these outcomes.
Men with intermediate risk prostate fall in between, and have a PSA between 10 and 20 ng/dl, a clinical stage of T2b, and a Gleason 7 grade. Men with this kind of cancer are likely to benefit from treatment (surgery, radiation, seeds) and do well with this treatment.